The Usefulness of Networks
What is a network for?
- To communicate
- To share resources
Network property
- transparency: the user does not know where the data is
- availability: increased if backup links are planned, if the network is meshed
- adaptability: easy to add posts
- reliability: absence of transmission errors
- security: password confidentiality
- performance: short response time, higher
OSI layered model:
1) Application layer
This is the program that needs the network to communicate
2) Presentation
It is responsible for the presentation of the data, independently of the microprocessor and the operating system ex: HTML
3) Session
She is in charge of establishing and maintaining the communication between the machines
4) Transportation
The transport layer is responsible for transporting the file segments. It has to cut a file into segments, to check that they have all arrived and to put them in order ex: TCP, UDP
5) The network layer
It is responsible for routing packets between remote endpoints across the network. Ex: IP
6) Liaison
Responsible for routing frames between two network nodes with flow control and error checking.
7) Physics
It handles coding or modulation to transmit bits
8) Physical support
It's not an OSI layer it's the cable or the fiber or the radio wave
Support:
Each layer uses the services of the layer below, and offers its services to the layer above.
DOD Model (Department of Defense)
This is the network model that was invented by the US military and evolved into the Internet. Compared to the OSI model, it is simplified.
Architecture of a network
Service
Customer
Protocol
Pilot
Windows station => network card => cable => HUB, switch or router.
Driver = communication between Operating System and Hardware
Protocol = Language in which machines communicate
TCP / IP, IPX, NETBEUI
TCP / IP: the most widespread and used on intern
IPX : coming from NOVELL
NETBEUI : for small networks, non-routable protocol
Client: software that allows communication with the service ex: client by Microsoft network.
The client is required to use shared resources
Service: Example: File or Printer Share
Sharing resources:
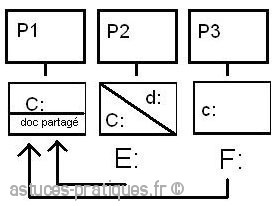
On P2: workstation: we can see A: / (diskette drive), C: / (system hard disk), D: / (data hard disk) and E: / (which is a shared folder of P1)
ON P2: C:> dir E: (Displays the contents of / P1 / doc P1doc shared (if C, a network drive)
To create a network drive:
-Command "connect a network drive" in windows
-net use e: / p1 / doc (in Cmd)
-net view: allows to see the resources available on the network.
Computer operation:
Dir> DOS> local disk
Dir> DOS> redirector> local disk or network





![[Darknet] How I Discovered It, and How to Access](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEigkvDILsG9sBTqEktFANKPS5HYpz1I4Cn00RhSPezewjQjxnKrznkJmBvWUnLHTrH_5_OibNQhzXA1HoPOKuhMOWkc5kaeA4QKpx5t24CS8rdr8YPqUGT4t8HogBdnS7Txj8p9AQZU7I0/s72-c/%255BDarknet%255D-How-I-Discovered-It%252C-and-How-to-Access.png)

Post a Comment